In recent years, the growing importance of sustainability in business has become increasingly evident. As consumers become more environmentally and socially conscious, companies are realizing the need to align their practices with these values.
Enter sustainability marketing – a powerful strategy for businesses to differentiate their brand, build customer loyalty, and drive positive change. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what sustainability marketing is, why it matters, and how companies can effectively implement it.
| Definition & Importance | Key Principles & Strategies | Examples & Challenges | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| – Promotes environmentally & socially responsible products, services, practices – Focuses on company mission & values to build long-term customer relationships – Important due to growing consumer demand, business benefits, positive societal & environmental impact | – Authenticity, transparency – Customer-centric approach – Holistic integration throughout business & supply chain – Continuous improvement & innovation – Storytelling, partnerships, sustainable product design, customer engagement | – Patagonia: strong environmental mission, “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign – Unilever: Sustainable Living Plan, “Real Beauty” campaign – Tesla: positioning EVs as high-performance & aspirational – Challenges: greenwashing risk, balancing sustainability & profitability, complex supply chains | – Increased regulation & standardization of sustainability claims – Shift towards regenerative & circular business models – Growing use of technology for measuring impact & engaging consumers |
- What is Sustainability Marketing?
- Why Sustainability Marketing Matters
- Key Principles of Sustainable Marketing
- Strategies for Effective Sustainability Marketing
- Examples of Brands Excelling in Sustainability Marketing
- Challenges and Criticisms of Sustainability Marketing
- The Future of Sustainability Marketing
- Conclusion
- Sustainable Marketing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is sustainability marketing?
- Why is sustainability marketing important?
- What are some key principles of effective sustainability marketing?
- How can companies tell authentic sustainability stories that resonate with consumers?
- What are some examples of brands excelling at sustainability marketing?
- How can companies avoid greenwashing in their sustainability marketing?
- What metrics should companies use to measure and report on sustainability progress?
- How can sustainability be integrated into product design and innovation?
- What does the future hold for sustainability marketing?
- How can companies engage employees and stakeholders around sustainability?
What is Sustainability Marketing?
At its core, sustainability marketing is the promotion of products, services, and practices that are environmentally and socially responsible. It goes beyond simply marketing “green” products and instead focuses on a company’s overall mission and values.
Green marketing aims to build long-term relationships with customers based on shared values and a commitment to making a positive impact on the world.
Key aspects of sustainability marketing include:
- Focusing on a company’s mission and values, not just products: Sustainable marketing requires a holistic approach that considers a company’s entire operations and supply chain. It’s not just about promoting eco-friendly products, but about embedding sustainability into the core of the business.
- Building long-term customer relationships based on shared values: Sustainability marketing seeks to connect with customers on a deeper level by appealing to their values and desire to make a difference. By consistently demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, companies can foster brand loyalty and advocacy.
- Encompassing environmental, social, and economic sustainability: True sustainability marketing considers the triple bottom line – people, planet, and profit. It recognizes that a company’s impact extends beyond just its environmental footprint and also includes its social and economic impact on communities and stakeholders.
It’s important to note that sustainability marketing differs from traditional marketing in several key ways. While traditional marketing often focuses on short-term sales and promoting specific products, sustainability marketing takes a longer-term view and emphasizes building brand trust and loyalty.
Additionally, sustainability marketing must be authentic and transparent to avoid being perceived as greenwashing – making misleading or false claims about a company’s environmental practices.

Key Takeaways
- Sustainability marketing promotes environmentally and socially responsible products, services, and practices to build long-term customer relationships based on shared values.
- It is driven by growing consumer demand, business benefits, and the potential for positive societal and environmental impact.
- Key principles include authenticity, transparency, customer-centricity, holistic integration, and continuous improvement.
- Effective strategies involve storytelling, partnerships, sustainable product design, and customer engagement.
- Leading examples include Patagonia’s strong environmental mission, Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan, and Tesla’s positioning of EVs as aspirational.
- Challenges include the risk of greenwashing, balancing sustainability with profitability, and navigating complex supply chains.
- The future will likely bring increased regulation, a shift towards regenerative and circular models, and the growing use of technology for measuring impact and engaging consumers.
- Engaging employees and stakeholders through education, involvement, and transparent communication is crucial for success.
Why Sustainability Marketing Matters
The rise of sustainable marketing is driven by several key factors, including:
- Growing consumer demand for sustainable products and practices: Studies consistently show that consumers, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, are increasingly prioritizing sustainability when making purchasing decisions. A recent survey found that nearly 80% of consumers are more likely to buy from companies that prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
- Benefits for businesses: Sustainability marketing offers numerous benefits for companies, including:
- Enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty
- Competitive advantage in crowded markets
- Cost savings through reduced waste and increased efficiency
- Attracting top talent who want to work for purpose-driven companies
- Positive impact on society and the environment: Perhaps most importantly, sustainability marketing has the potential to drive meaningful change by:
- Encouraging responsible consumption and production
- Supporting social causes and community development
- Contributing to the transition to a more sustainable economy
By aligning their marketing efforts with sustainability principles, companies can not only boost their bottom line but also make a positive impact on the world.
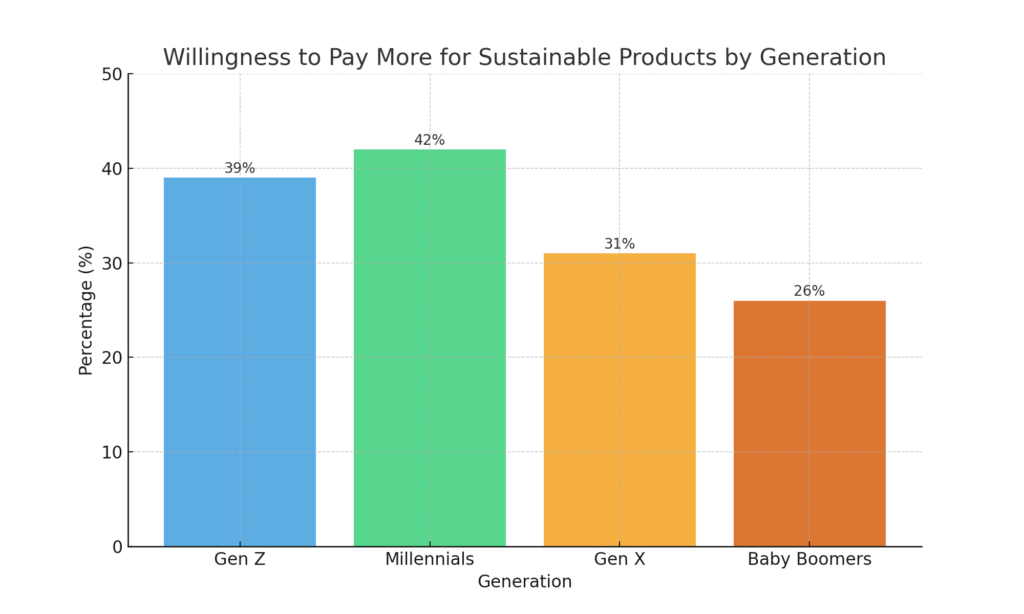
Key Principles of Sustainable Marketing
To effectively implement sustainability marketing, companies should follow these key principles:
- Authenticity and transparency: Sustainability marketing must be grounded in genuine commitment and action. Companies should align their marketing messages with their actual sustainability efforts and avoid making misleading or exaggerated claims. Transparency about a company’s progress and challenges is crucial for building trust with consumers.
- Customer-centric approach: Effective sustainability marketing requires understanding and addressing customer needs and values. Companies should engage with customers to learn what sustainability issues matter most to them and educate them on how their products and practices make a difference.
- Holistic integration: Sustainability marketing should not be a siloed effort, but rather integrated throughout the entire business. This means considering sustainability at every stage of the product life cycle, from sourcing materials to end-of-life disposal, and engaging all departments in the sustainability mission.
- Continuous improvement: Sustainability is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Companies should set measurable sustainability goals, track their progress, and continuously innovate to find new ways to reduce their environmental impact and create positive social change.
By following these principles, companies can create sustainability marketing campaigns that are authentic, impactful, and resonate with consumers.

Strategies for Effective Sustainability Marketing
Now that we’ve covered the basics of what sustainability marketing is and why it matters, let’s dive into some practical strategies for implementing it effectively.
From storytelling to partnerships to product design, there are many ways companies can integrate sustainability into their marketing efforts in a way that resonates with consumers and drives real impact.
Storytelling and Emotional Connection
One of the most powerful tools in green marketing is storytelling. By sharing the company’s sustainability journey – the challenges, successes, and lessons learned along the way – brands can create an emotional connection with consumers and inspire them to join the cause.
Patagonia is a master of this approach. The outdoor apparel company regularly shares stories about its environmental activism, supplier relationships, and product innovations on its blog, social media, and even product tags. These stories help customers feel like they are part of something bigger when they buy Patagonia gear.
Another effective storytelling tactic is highlighting the sustainability stories of customers and employees. Featuring real people who are passionate about sustainability – whether it’s a customer who repairs their clothes instead of buying new or an employee who leads a beach cleanup – can make the issue feel more relatable and inspire others to get involved.

Partnerships and Collaborations
No company can tackle sustainability alone. That’s why partnerships and collaborations are crucial for credibility and impact in sustainability marketing. By working with respected environmental and social organizations, brands can tap into their expertise, networks, and legitimacy.
One example is Unilever’s partnership with the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) to reduce the environmental impact of its agricultural supply chain. By working with WWF to develop sustainable sourcing guidelines and train farmers, Unilever is not only improving its own practices but also driving industry-wide change.
Brands can also join larger industry initiatives and certifications to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. For example, the Sustainable Apparel Coalition’s Higg Index provides a standardized way for fashion brands to measure and share their environmental and social impact.
By participating in these initiatives, companies can collaborate with peers, learn best sustainable marketing practices, and communicate their progress to consumers.
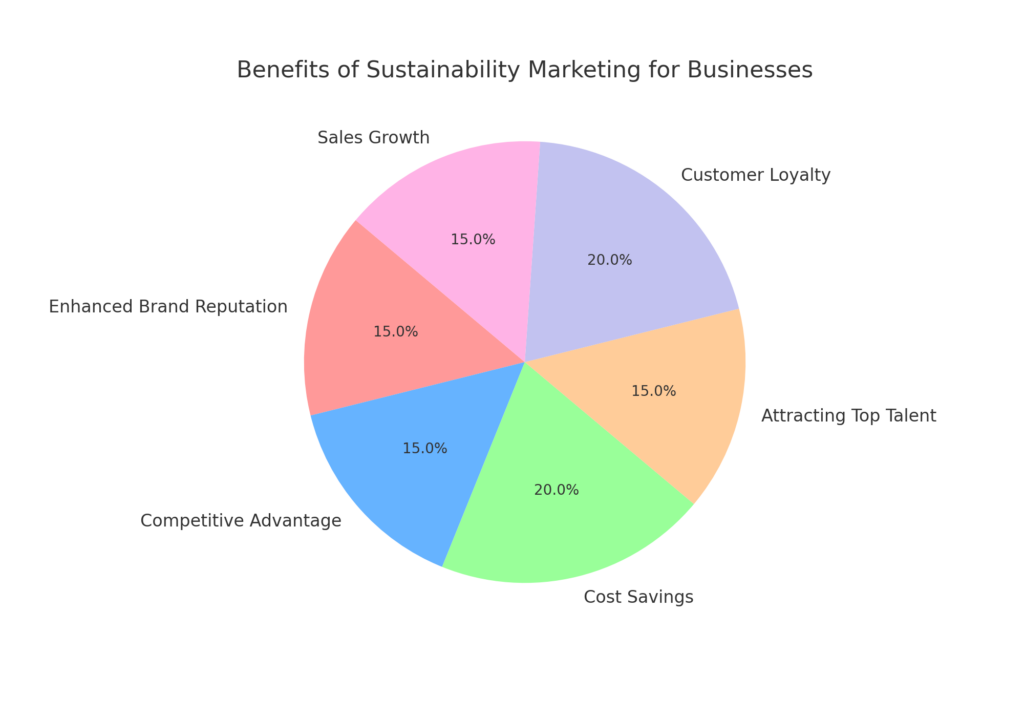
Sustainable Product Design and Packaging
Of course, sustainable marketing must be backed up by sustainable products. Companies should consider the environmental impact of their products at every stage of the life cycle, from the materials used to the manufacturing process to the end-of-life disposal.
Using eco-friendly materials like organic cotton, recycled polyester, or biodegradable packaging can reduce a product’s environmental footprint and appeal to conscious consumers. Designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability can also help minimize waste and promote a circular economy.
When it comes to communicating product sustainability to consumers, transparency is key. Companies should clearly explain the sustainable features and benefits of their products and services, backed up by third-party certifications where relevant.
Patagonia’s “Footprint Chronicles” microsite, for example, allows customers to trace the social and environmental impact of specific products from raw materials to finished goods.

Engaging and Empowering Customers
Finally, sustainability marketing should not just be about selling products, but about engaging and empowering customers to live more sustainably in their own lives. By providing resources, incentives, and inspiration for sustainable behaviors, brands can amplify their impact beyond their own operations.
One way to do this is through educational content and sustainable marketing campaigns. Unilever’s “Sustainable Living” website, for example, provides tips and tools for reducing household waste, saving energy and water, and supporting local communities. The site also showcases Unilever’s progress towards its sustainability goals, making the connection between individual actions and larger impact.
Brands can also use their marketing channels to encourage specific sustainable behaviors. Patagonia’s “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign, which encouraged customers to repair and reuse their existing clothing instead of buying new, is a famous example.
Other tactics could include promoting product take-back programs, offering discounts for sustainable actions, or gamifying sustainability challenges.
By engaging and empowering customers in these ways, sustainability marketing can create a ripple effect of positive change beyond just the company’s own footprint.
Examples of Brands Excelling in Sustainability Marketing
To bring these sustainable marketing strategies to life, let’s take a closer look at a few brands that are leading the way in sustainability marketing.
Patagonia
Patagonia is often held up as the gold standard of sustainability marketing, and for good reason. The outdoor apparel company has integrated sustainability into every aspect of its business, from its product design and supply chain to its activism and customer engagement.
Some key examples of Patagonia’s sustainable marketing include:
- “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign: In a bold move, Patagonia ran a full-page ad in the New York Times on Black Friday 2011 with the headline “Don’t Buy This Jacket.” The ad copy urged consumers to think twice before buying new gear and promoted Patagonia’s Common Threads Initiative, which encourages customers to repair, reuse, and recycle their clothing. The campaign generated buzz and cemented Patagonia’s reputation as a leader in sustainable consumption.
- Worn Wear program: Patagonia’s Worn Wear program takes back used Patagonia gear, repairs it, and resells it at a discount. The program keeps clothing in use longer, reduces waste, and provides an affordable entry point for customers. Patagonia has even hosted Worn Wear pop-up events where customers can get their gear repaired on the spot.
- 1% for the Planet: Patagonia was one of the first companies to join 1% for the Planet, pledging to donate 1% of its sales to environmental organizations. To date, the company has donated over $140 million to grassroots environmental groups. This commitment helps Patagonia build credibility with environmentally conscious consumers and use its platform to drive change.
Unilever
Unilever, one of the world’s largest consumer goods companies, has also made sustainability a core part of its business strategy and marketing. Some examples include:
- Sustainable Living Plan: In 2010, Unilever launched its Sustainable Living Plan, which set ambitious goals for improving the health and well-being of people around the world while reducing the company’s environmental impact. The plan includes targets for sustainable sourcing, waste reduction, and social impact, and progress is reported publicly each year.
- “Real Beauty” campaign: Dove, one of Unilever’s largest personal care brands, has built its marketing around the concept of “Real Beauty.” The campaign challenges narrow beauty standards and celebrates diversity and self-esteem. While not explicitly environmental, the campaign aligns with Unilever’s broader sustainability mission and has been praised for its positive social impact.
- Product innovation: Unilever has also focused on developing more sustainable products, such as concentrated laundry detergents that reduce packaging waste and plant-based food products that have a lower environmental footprint than animal proteins. By integrating sustainability into its product innovation pipeline, Unilever is able to offer consumers more sustainable choices.
Tesla
While Tesla is a car company, not a consumer products brand, its marketing has played a significant role in shifting perceptions of sustainable transportation. Some key examples include:
- Positioning sustainability as aspirational: Tesla has marketed its electric vehicles not just as an eco-friendly alternative to gas-powered cars, but as a sleek, high-performance luxury brand. By making sustainability synonymous with style and innovation, Tesla has broadened the appeal of EVs and accelerated the shift away from fossil fuels.
- Insider referral program: Tesla has relied heavily on word-of-mouth marketing, driven by its enthusiastic customer base. The company’s referral program rewards customers for referring new buyers, creating a network of brand ambassadors who are passionate about Tesla’s mission.
- Supercharger network: To address concerns about EV charging infrastructure, Tesla has built out its own global network of Supercharger stations. The network not only makes long-distance EV travel more feasible, but also serves as a visible symbol of Tesla’s commitment to sustainability.
These examples demonstrate the power of integrating sustainability into every aspect of a brand’s marketing strategy, from messaging to product innovation to customer engagement.
Challenges and Criticisms of Sustainability Marketing
While sustainability marketing has the potential to drive significant positive impact, it is not without its challenges and criticisms.
Risk of Greenwashing and Consumer Skepticism
One of the biggest risks of green marketing is greenwashing – making false or misleading claims about a company’s environmental practices. As consumers become more savvy and skeptical of corporate sustainability claims, companies must be careful to back up their marketing with real, verifiable actions and results.
The key to avoiding greenwashing is transparency and specificity. Rather than making vague claims about being “eco-friendly,” companies should share specific, measurable goals and progress. Third-party certifications, such as B Corp or Fair Trade, can also help build credibility.
Balancing Sustainability with Profitability and Growth
Another challenge of sustainability marketing is balancing sustainability goals with business realities. Implementing sustainable practices can be costly and may require trade-offs in terms of profitability or growth.
However, many companies are finding ways to create shared value – solutions that benefit both the bottom line and society. For example, reducing waste and increasing efficiency can lower costs while also reducing environmental impact. And as consumer demand for sustainable products grows, sustainability can be a competitive advantage that drives sales and brand loyalty.
Complexity of Global Supply Chains and Environmental Impacts
Finally, the complexity of global supply chains can make it difficult for companies to fully understand and address their environmental and social impacts. Many consumer products have long, multi-tiered supply chains that span multiple countries and involve numerous suppliers.
To address this challenge, companies need to invest in supply chain transparency and collaboration. This may involve using new technologies like blockchain to track materials and products from source to shelf, or working with industry partners to develop shared sustainability standards and best practices.
Ultimately, sustainability marketing requires a long-term, holistic approach that considers the entire lifecycle of a product and the full scope of a company’s impact. It requires leadership buy-in, cross-functional collaboration, and a willingness to continuously improve and innovate.
The Future of Sustainability Marketing
As the urgency of climate change and other sustainability challenges grows, so too does the importance of sustainability marketing. Here are some key trends and predictions for the future of the field:
Increasing Regulation and Standardization
As more companies adopt sustainability marketing practices, there will likely be increasing pressure for regulation and standardization to ensure transparency and accountability. This may include mandatory sustainability reporting, similar to financial reporting, or industry-wide standards for measuring and communicating environmental and social impact.
The development of frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) is already helping to create a common language and set of metrics for sustainability reporting. As these frameworks mature and gain wider adoption, they will help level the playing field and make it easier for consumers to compare companies’ sustainability performance.
Shift Towards Regenerative and Circular Business Models
While much of sustainability marketing to date has focused on reducing negative environmental impacts, there is a growing recognition that this is not enough. To truly create a sustainable future, companies need to go beyond “less bad” and actively work to restore and regenerate ecosystems and communities.
This shift is already underway, with a growing number of companies adopting circular economy principles and investing in regenerative agriculture, renewable energy, and other solutions that create positive environmental and social impact. As these approaches gain traction, sustainability marketing will need to evolve to communicate these more complex and systemic solutions to consumers.
Growing Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation will play an increasingly important role in sustainability marketing in the years ahead. From using data and AI to measure and optimize sustainability performance, to developing new sustainable materials and production methods, technology will be a key enabler of more sustainable business practices.
At the same time, technology is also changing the way companies engage with consumers around sustainability. Digital platforms and social media have made it easier than ever for brands to share their sustainability stories and engage customers in dialogue and action. Emerging technologies like augmented reality and blockchain may also create new opportunities for transparency, traceability, and consumer engagement.
As technology continues to evolve, sustainability marketers will need to stay on the cutting edge and find new ways to leverage these tools to drive impact and build brand value.
Conclusion
Sustainability marketing is a rapidly evolving field that holds immense potential for driving positive change. By aligning marketing strategies with sustainability goals, companies can not only build brand loyalty and competitive advantage, but also contribute to a more just and sustainable future for all.
However, realizing this potential will require more than just a few ad campaigns or product labels. It will require a fundamental shift in the way companies think about their role in society and their responsibility to the planet and future generations.
The examples of sustainable marketing and strategies outlined in this article provide a roadmap for companies looking to embed sustainability into their marketing efforts. From authentic storytelling and strategic partnerships, to sustainable product innovation and customer empowerment, there are many ways to create shared value and drive meaningful impact.
But sustainability marketing is not a one-time initiative or a box to be checked. It is an ongoing journey that requires leadership, collaboration, and a willingness to continuously learn and adapt. As the stakes of the sustainability crisis continue to rise, the role of marketing in shaping a more sustainable future will only become more important.
The question is not whether companies can afford to prioritize sustainability in their marketing, but whether they can afford not to.
Sustainable Marketing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is sustainability marketing?
Sustainability marketing promotes products, services, and practices that are environmentally and socially responsible. It focuses on a company’s overall mission and values to build long-term customer relationships based on shared sustainability commitments.
Why is sustainability marketing important?
Sustainability marketing is crucial due to growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, the competitive advantages and cost savings it provides businesses, and its positive impact on society and the environment through encouraging responsible consumption and production.
What are some key principles of effective sustainability marketing?
Key principles include authenticity and transparency, a customer-centric approach that educates and engages, holistic integration of sustainability throughout the business and supply chain, and a commitment to continuous improvement and innovation.
How can companies tell authentic sustainability stories that resonate with consumers?
Companies can share their sustainability journey, challenges, and impact through highlighting customer and employee stories, forming strategic partnerships with environmental organizations, and transparently communicating progress towards measurable sustainability goals.
What are some examples of brands excelling at sustainability marketing?
Patagonia, with its strong environmental mission and bold “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign; Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan and “Real Beauty” campaigns; and Tesla, positioning electric vehicles as high-performance and aspirational, are all powerful examples.
How can companies avoid greenwashing in their sustainability marketing?
To avoid greenwashing, companies must back up sustainability claims with real, measurable actions and results, be transparent about challenges and progress, and seek out credible third-party certifications and partnerships.
What metrics should companies use to measure and report on sustainability progress?
Key sustainability metrics include carbon footprint, energy and water usage, waste reduction, sustainable sourcing, and social impact. Reporting frameworks like GRI and SASB help standardize disclosures. Regular sustainability reports build trust and accountability.
How can sustainability be integrated into product design and innovation?
Sustainable product design considers environmental impact across the lifecycle, from materials sourcing to end-of-life. Strategies include using recycled or bio-based inputs, designing for recyclability/reuse, reducing packaging waste, and prioritizing energy efficiency.
What does the future hold for sustainability marketing?
The future will likely bring increased regulation and standardization of sustainability claims, a shift towards regenerative and circular business models that restore ecosystems, and the growing use of technology for measuring impact and engaging consumers.
How can companies engage employees and stakeholders around sustainability?
Engaging employees requires education, involvement in sustainability initiatives, and cultivating a culture of shared responsibility. Communicating transparently, seeking input, and collaborating on solutions are key to bringing stakeholders on the sustainability journey.
